Cloud computing is a type of computing that relies on sharing computing resources rather than having
local servers or personal devices to handle applications.
In cloud computing, the word cloud (also
phrased as "the cloud") is used as a metaphor for "the Internet," so the phrase cloud computing means "a type of
Internet-based computing," where different services — such as servers, storage and applications. —are delivered to an organization's computers and devices
through the Internet.
Cloud computing is comparable to grid computing,
a type of computing where unused processing cycles of all computers in a
network are harnesses to solve problems too intensive for any stand-alone
machine.
The
world of the cloud has lots of participants:
· The
end user who doesn’t have to know anything about the underlying technology.
Business
management who needs to take responsibility for the governance of data or
services living in a cloud. Cloud service providers must provide a predictable
and guaranteed service level and security to all their constituents.
· The
cloud service provider who is responsible for IT assets and maintenance.

Advantages of cloud computing
1. Worldwide Access.
Cloud computing increases mobility, as you can access your documents from any
device in any part of the world. For businesses, this means that employees
can work from home or
on business trips, without having to carry around documents. This increases
productivity and allows faster exchange of information. Employees can also work
on the same document without having to be in the same place.
2. More Storage. In the past, memory was limited by the
particular device in question. If you ran out of memory, you would need a USB
drive to backup your current device. Cloud computing provides increased
storage, so you won’t have to worry about running out of space on your hard
drive.
3. Easy Set-Up. You can set up a cloud computing service
in a matter of minutes. Adjusting your individual settings, such as choosing
a password or
selecting which devices you want to connect to the network, is similarly
simple. After that, you can immediately start using the resources, software, or
information in question.
4. Automatic Updates. The cloud computing provider is
responsible for making sure that updates are available – you just have to download them.
This saves you time, and furthermore, you don’t need to be an expert to update
your device; the cloud computing provider will automatically notify you and
provide you with instructions.
5. Reduced Cost. Cloud computing is often inexpensive. The
software is already installed online, so you won’t need to install it yourself.
There are numerous cloud computing applications available
for free, such as Dropbox, and increasing storage size and memory is
affordable. If you need to pay for a cloud computing service, it is paid for
incrementally on a monthly or yearly basis. By choosing a plan that has no
contract, you can terminate your use of the services at any time; therefore,
you only pay for the services when you need them
The working principle of cloud
computing
The principle of cloud computing
is almost same with another computer, just the different of that is in
cloud computing, is coupled with another present computer. In regular
computer, file from
software when we used is stored in hardisk or another storage media. But on
computer clouds if viewed from the side of the user, the files from software we
use is in another computer.
In other words we are connected to
multiple computers on a network server, but the data we store it was in the
data center or in center, so that not only we can open the file that
we save but computers or other users can open it and vice versa (Public). Also
in a lot of infrastructure servers that we can use and we only pay as needed.
1. On-demand self-service. This means provisioning or de-provisioning
computing resources as needed in an automated fashion without human
intervention. An analogy to this is electricity as a utility where a consumer
can turn on or off a switch on-demand to use as much electricity as required.
2. Ubiquitous network access. This means that computing facilities can be accessed
from anywhere over the network using any sort of thin or thick clients (for
example smartphones, tablets, laptops, personal computers and so on).
3. Resource pooling. This
means that computing resources are pooled to meet the demand of the consumers
so that resources (physical or virtual) can be dynamically assigned,
reassigned or de-allocated as per the requirement. Generally the consumers are
not aware of the exact location of computing resources. However, they may be
able to specify location (country, city, region and the like) for their need.
For example, I as a consumer might want to host my services with a cloud
provider that has cloud data centers within the boundaries of Australia.
4. Rapid elasticity. Cloud
computing provides an illusion of infinite computing resources to the users. In
cloud models, resources can be elastically provisioned or released according to
demand. For example, my cloud-based online services should be able to handle a
sudden peak in traffic demand by expanding the resources elastically. When the
peak subsides, unnecessary resources can be released automatically.
5. Measured service. This means that consumers only pay for the computing
resources they have used. This concept is similar to utilities like water or
electricity.
SECURITY
Security.
When using a cloud computing service, you are essentially handing over your
data to a third party. The fact that the entity, as well as users from all over
the world, are accessing the same server can cause a security issue. Companies
handling confidential information might be particularly concerned about using
cloud computing, as data could possibly be harmed by viruses and other malware.
That said, some servers like Google Cloud Connect come with customizable spam
filtering, email encryption, and SSL enforcement for secure HTTPS access,
among other security measures.
The biggest question most have
with Cloud Computing is will it be Safe? The answer is “NO” Reason why is everything that
Cloud Computing
is based on is mechanical, although it seems virtual. The Safety of the data
(information), is only as Safe as the will and determination of the individual
that wants to have at it.
THE CONCEPT OF CLOUD COMPUTING
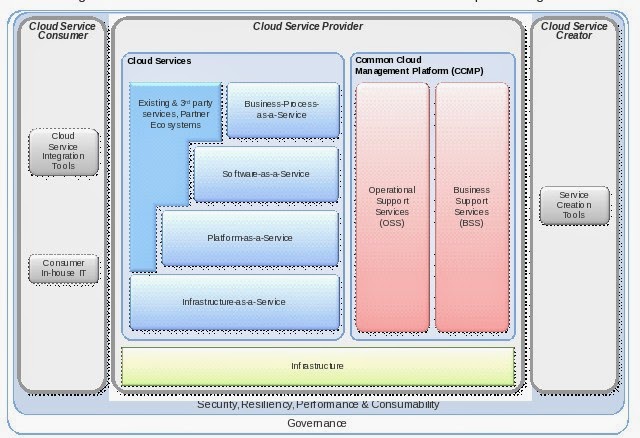
The first building block is the infrastructure where
the cloud will be implemented. Some people make the assumption that environment
should be virtualized, but as cloud is a way to request resources
in an on-demand way and if you have solutions to provide on bare metal,
then why not? The infrastructure will support the different types of cloud
(IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, BPaaS).
To be able to provide these services you will need
Operating System Services (OSS), which will be in charge of deploying the
requested service, and Business System Services (BSS), mainly used to validate
the request and create the invoice for the requested services. Any metrics
could be used to create the invoice (for example, number of users, number of
CPUs, memory, usage hours/month). It is very flexible and depends on the
service provider.
A cloud computing environment will also need to
provide interfaces and tools for the service creators and users. This is the
role of the Cloud Service Creator and Cloud Service Consumer components.
Now,
let’s see how it works in reality.
Generally, you log in to
a portal (enterprise or public wise) and you order your services through the
Cloud Service Consumer. This service has been created by the cloud service
provider and can be a simple virtual machine (VM) based on an image, some
network components, an application service such as an WebApp environment and a
service such as MongoDB. It depends on the provider and type of resources and
services.
The cloud provider will validate, through the BSS,
your request and if the validation is okay (credit card, contract), it will
provision the request through the OSS.
You
will receive, in one way or another, the credentials to access your
requested services and you will usually receive a monthly invoice for your
consumption.
http://thoughtsoncloud.com/2014/02/how-does-cloud-computing-work/
http://thoughtsoncloud.com/2014/02/cloud-computing-basics/
http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/what-is-cloud-computing.html
http://www.wikinvest.com/concept/Cloud_Computing
http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/C/cloud_computing.html



